Engineering With Java: Digest #57
Handpicked and Curated: The Best Java and Spring Blogs.
Introduction
This week’s collection includes articles related to resilient microservice architectures and powerful JVM diagnostics to advanced AI integrations and new language APIs, the landscape offers numerous opportunities to level up your development skills and system performance.
We cover weekly exciting Spring Boot and Java articles that are worth reading as a Java engineer. Subscribe to get notifications of new articles every week!
Self-Healing Microservices: Implementing Health Checks with Spring Boot and Kubernetes
This article explains how to build resilient microservices that automatically recover from failures. It focuses on using Spring Boot’s actuator health checks and Kubernetes liveness and readiness probes to monitor service health. When a service is unhealthy, Kubernetes can restart it (self-healing). The article also covers customizing health indicators and how proper probe configurations ensure high availability and minimal downtime.
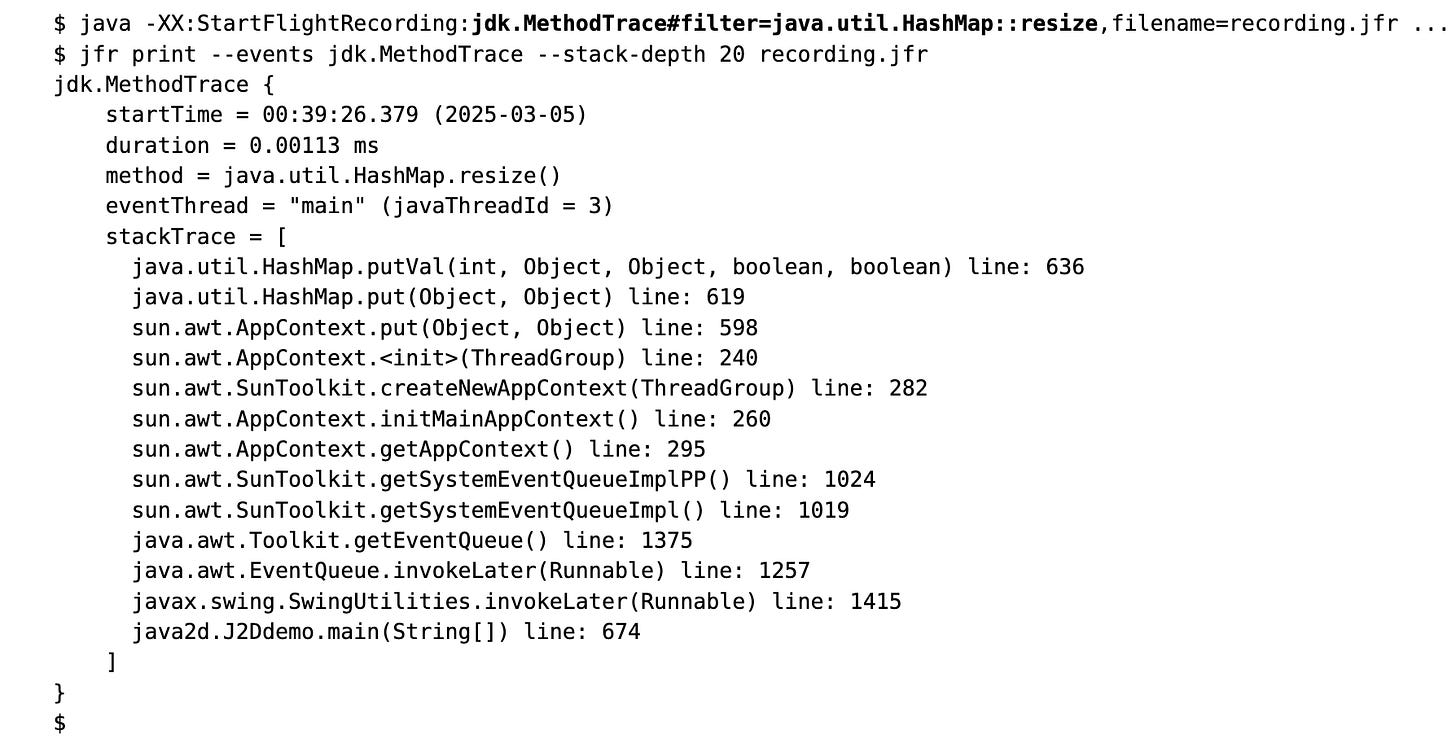
JEP targeted to JDK 25: 520: JFR Method Timing & Tracing
JEP 520 adds two new events to the Java Flight Recorder (JFR): jdk.MethodTiming and jdk.MethodTrace, enabling built‑in method execution timing and tracing within the JVM via bytecode instrumentation, without external profilers or agent. This Enables developers to track method execution counts and durations (MethodTiming) and capture detailed call stacks (MethodTrace) for selected methods in testing and production environments.
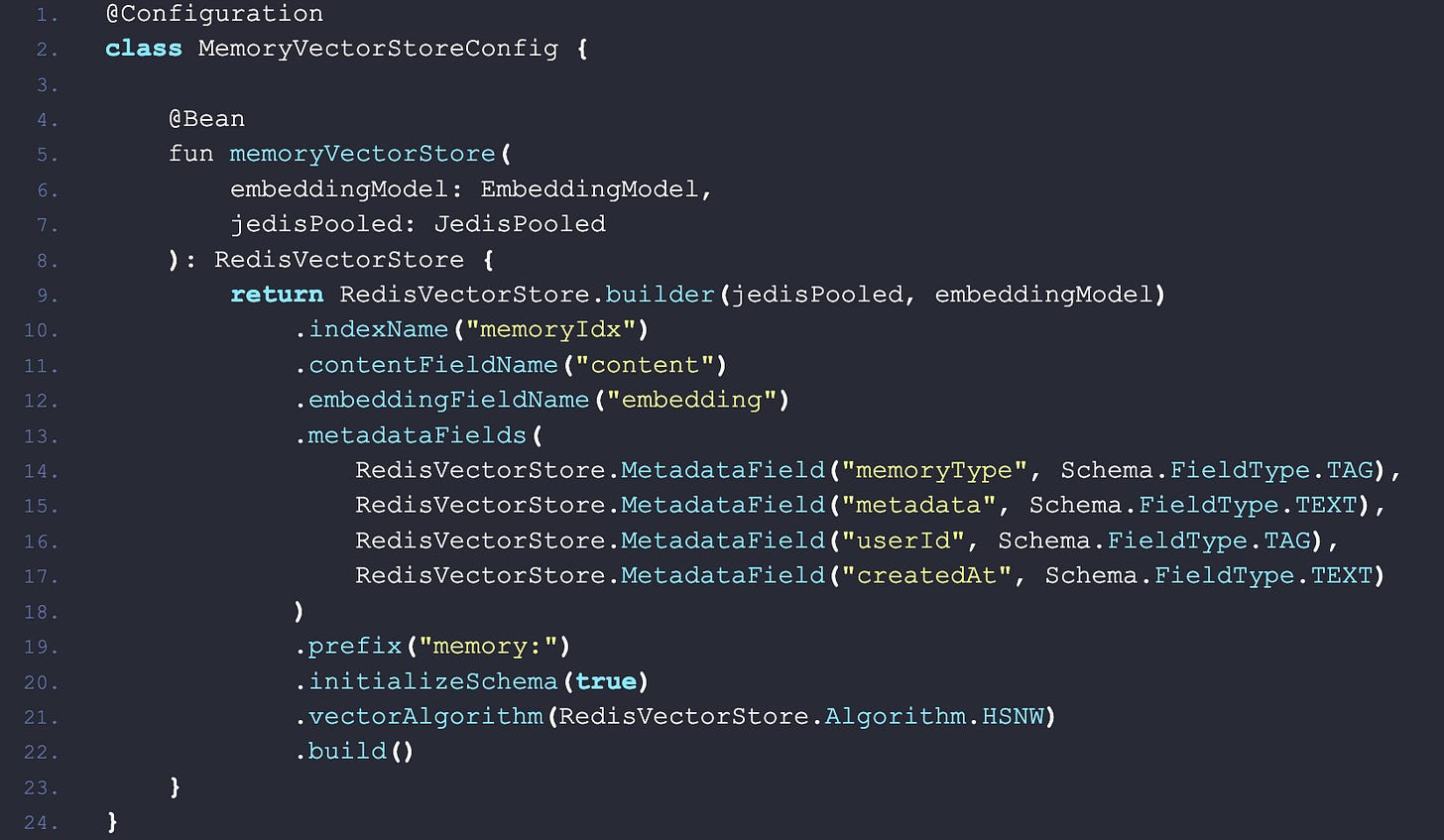
Agent Memory with Spring AI & Redis
The article walks through building a memory-enabled AI agent using Spring Boot, Spring AI, and Redis, enabling both short-term and long-term memory for personalized interactions. Standard LLMs are stateless—they don’t retain user context across conversations. By contrast, memory-enabled agents recall user details, preferences, and past interactions, creating richer and more tailored responses. Example: remembering a shellfish allergy when suggesting restaurants in Boston.
A Sneak Peek at the Stable Values API
A new API introduced in JDK 25 via JEP 502, Stable Values bring deferred immutability: objects that are computed at most once and afterward behave like final constants—even though they’re initialized lazily. Internally, they mirror the functionality of Oracle’s internal @Stable annotation, now safely exposed to external Java developers. StableValue<T> holds a single value that gets computed once via .orElseSet(...). Afterward, it’s effectively immutable—and constant-foldable by the JVM.
static final StableValue<Logger> logger = StableValue.of();
logger.orElseSet(() -> Logger.create(...));
Java 22 to 24: Level up your Java Code by embracing new features in a safe way
This article highlights key features from Java 22 to 24—like unnamed variables, pattern matching with primitives, structured concurrency, and the Foreign Function & Memory API. It shows how to adopt these features safely using tools like SonarQube to modernize code while maintaining reliability and readability
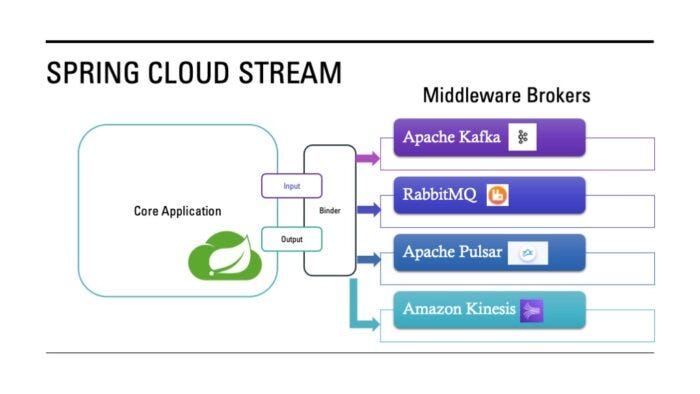
Spring Cloud Stream: Event-Driven Architecture – Part 1
This article introduces Spring Cloud Stream as a powerful abstraction for building event-driven microservices using brokers like Kafka or RabbitMQ, without coupling business logic to specific messaging technologies. It explains how producers, consumers, and processors communicate asynchronously via events, enabling loose coupling, scalability, and resilience. By leveraging binders, channels, and message schemas, Spring Cloud Stream simplifies integration with messaging systems and promotes a clean, maintainable architecture for real-time data flow.
Undocumented Java 16 Feature: The End-of-File Comment
In Java 16 and later, inserting the Unicode end‑of‑file character \u001a anywhere in a source file causes the compiler to ignore everything that follows—effectively a silent “comment” until the file's end. Originally intended only at a file’s end, this undocumented quirk lets you truncate code, suppressing compilation of subsequent declarations or constructs.
Service Mesh in Java: Istio and Linkerd Integration for Secure Microservices
This article explains how integrating a service mesh—specifically Istio or Linkerd—enhances Java microservices in Kubernetes with automatic mutual TLS (mTLS) encryption, advanced traffic shaping capabilities (like canary releases and traffic splits), and built-in observability through metrics, tracing, and dashboards, all without modifying application code.
To get fresh and interesting Java and Spring Boot articles in your feed, subscribe to the Java newsletter.