Engineering With Java: Digest #70
Best of blogs, articles, code samples and interview questions
👋 Java Devs! Welcome to this week’s addition! Merry Christmas & Happy Holidays!!
I am sure you all are doing awesome!
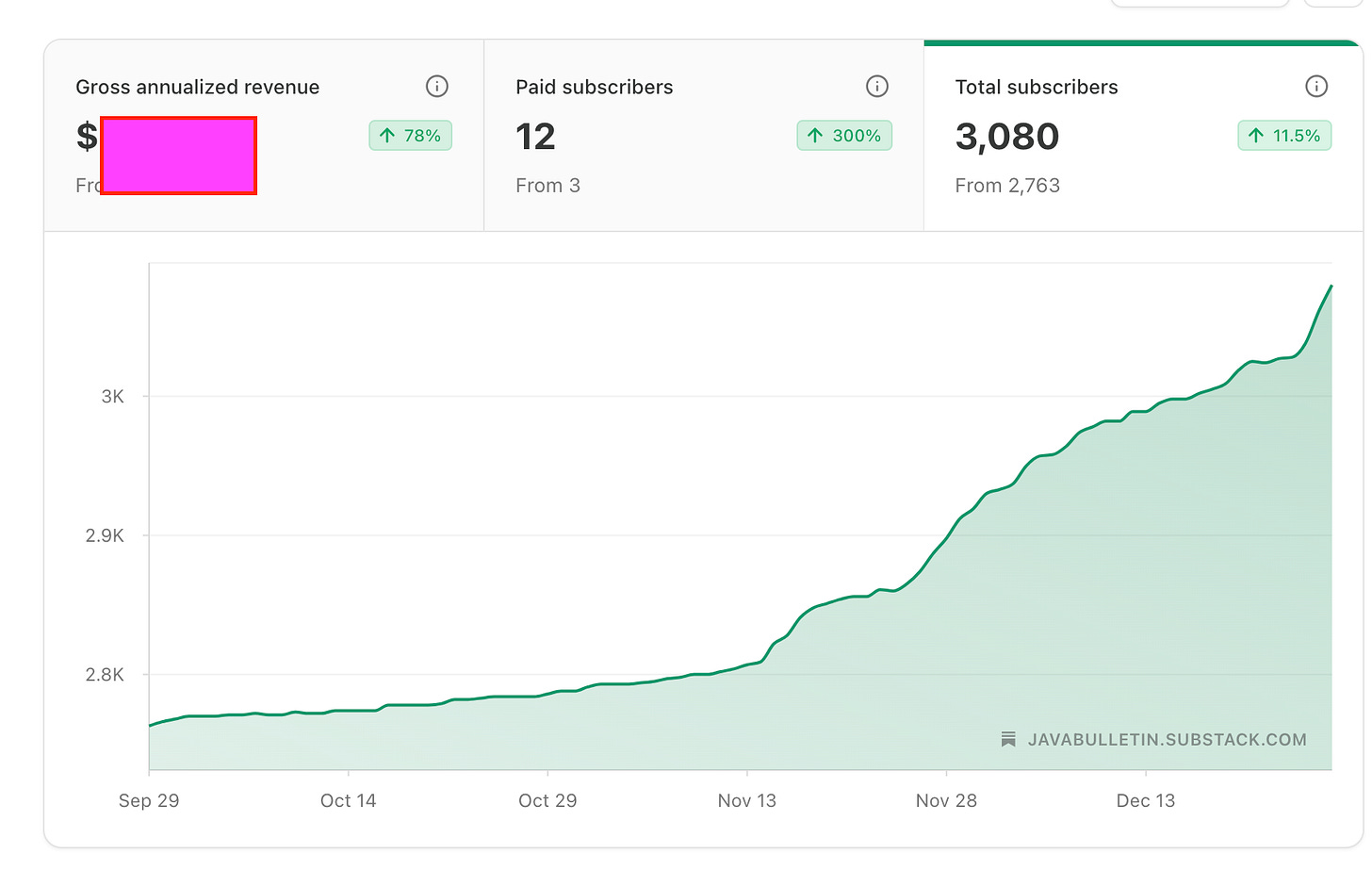
We’ve surpassed 3,000 subscribers this year 🥳! I’m grateful to every one of you for giving your time to read this newsletter. A special thanks to the 12 amazing readers who upgraded to a paid subscription—your support means a lot. My goal remains to grow a thriving Java community that learns together and also helps non-Java developers break into this world.
At the end of the newsletter, I have a gift for you all, don’t cheat 😉 and keep reading till the end!
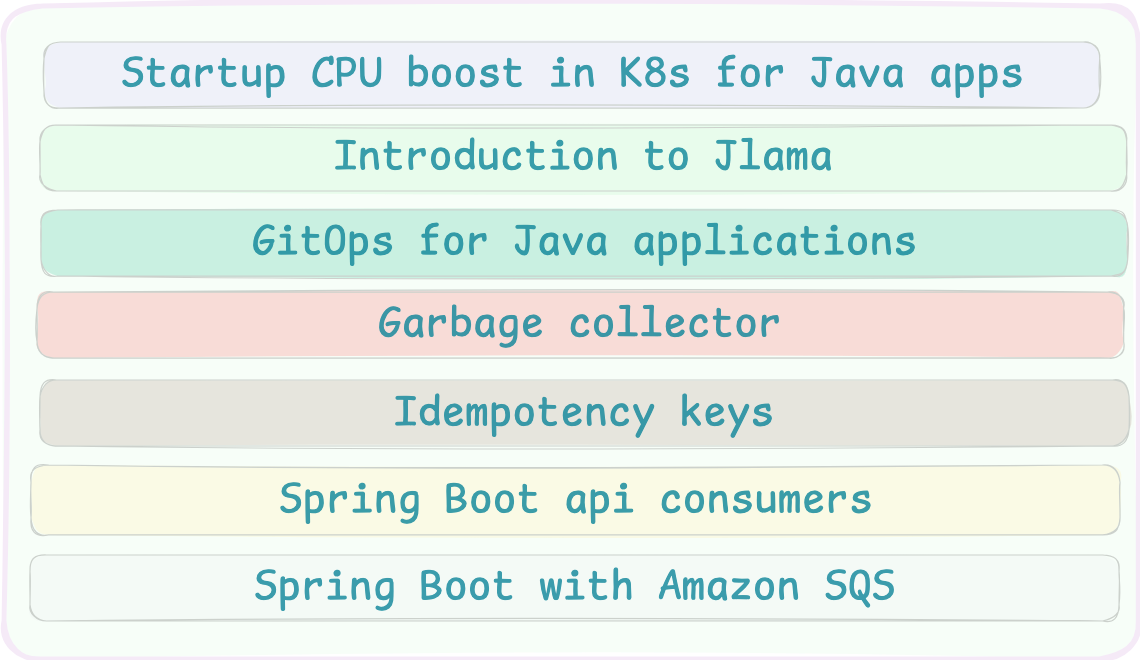
This week, we cover essential insights on:
Startup CPU boost in Kubernetes for Java apps
Introduction to Jlama
GitOps for Java applications
Garbage collector
Idempotency keys
Spring Boot api consumers
Spring Boot with Amazon SQS
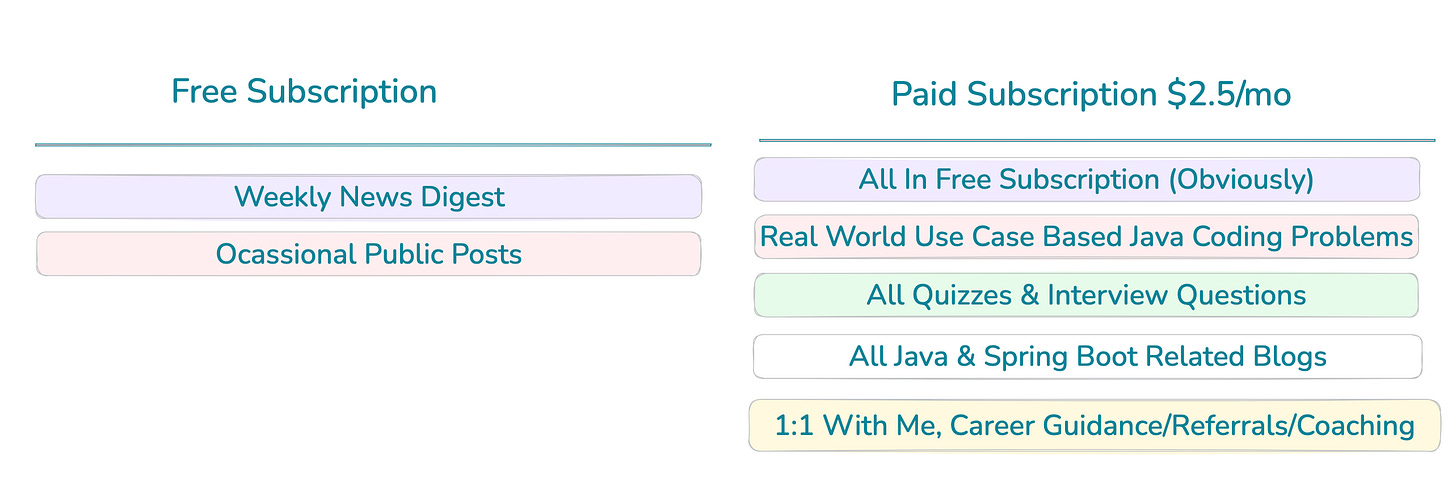
📢 Consider becoming paid subscriber for as low as $2.5/mo (with an annual subscription) and support the work :)
Not convinced? Check out the details of the past work
🗒️ Articles Of The Week (7)
Startup CPU Boost in Kubernetes with In-Place Pod Resize: This article explains how to speed up startup performance for containers in Kubernetes by combining Kubernetes’ In‑Place Pod Resize feature with Kube Startup CPU Boost, allowing pods to temporarily scale up their CPU allocation during startup and then reduce it afterward. This approach is particularly useful for Java applications, which often need more CPU at launch than during steady state, helping them start faster without permanently overprovisioning resources. By adjusting CPU limits in place rather than redeploying pods, teams can improve startup latency while keeping overall cluster resource usage efficient.
Introduction to Jlama: Introduces Jlama, a Java-based LLM inference engine that lets us run pre-trained large language models locally in a Java application without relying on external APIs. It shows how to add Jlama to a Maven project, configure the JVM for preview features like the Vector API, download a model from Hugging Face, and use the Jlama API to generate text from a prompt. With this setup, developers can quickly experiment with LLMs and build AI-powered features directly in Java.
GitOps for Java Applications: Continuous Delivery Reimagined: GitOps reimagines continuous delivery for Java apps by making Git the single source of truth for deployments, infrastructure, and environment configuration. Tools like ArgoCD and Flux reconcile the desired state in Git with what’s actually running, enabling automation, reliability, observability, and easy rollbacks. This approach improves security, consistency, and delivery speed, especially for Java applications deployed on Kubernetes and cloud-native environments.
Understanding JAVA Garbage Collectors: Java’s garbage collection automatically frees memory by removing objects that are no longer reachable, helping prevent memory leaks and reducing developer overhead. The article explains major GC types—Serial, Parallel, CMS, G1, ZGC, and Shenandoah—highlighting how each balances throughput, latency, and pause times. It also stresses choosing the right GC, tuning JVM options, and monitoring GC behavior to improve application performance.
Soft Quotas for Spring Boot API Consumers: Spring Boot soft quotas help APIs pace client requests by giving gentle warnings before strict limits are hit, so clients can slow down without abrupt cutoffs. The approach tracks request activity in sliding time windows, using lightweight counters per client (e.g., by API key or token) to monitor request rates and emit hint headers when a soft threshold is approaching. Filters implement this logic early in the request pipeline, optionally backed by shared stores like Redis for distributed fairness, and only enforce a hard limit (e.g., 429 responses) once the quota is truly exceeded.
How to Integrate Spring Boot 3 with Amazon SQS Using AWS SDK v2: Spring Boot 3 can be integrated with Amazon SQS using AWS SDK v2 by adding the AWS SQS client dependency (software.amazon.awssdk:sqs) and configuring an SqsClient bean with region and credentials to send and receive messages. We then write service code that sends messages via sendMessage and polls or receives messages with receiveMessage, handling deletion after processing to prevent re‑delivery. For more automated message consumption, we can also add Spring Cloud AWS Starter for SQS and use @SqsListener to let Spring handle polling and listener invocation for the queues.
On Idempotency Keys: This article explains idempotency keys, which ensure exactly-once processing by letting systems detect and ignore duplicate requests, storing the key with the result for retries. It covers strategies like random UUIDs, monotonically increasing sequences, and log-derived keys, each with trade-offs in storage, concurrency, and efficiency. Choosing the right approach depends on system scale and requirements, balancing simplicity, performance, and reliable duplicate detection.
Recently Published In-house Blogs (4)
▶️ Videos Of The Week (3)
Jump-Start Your Data Science Learning Java & Jupyter Notebooks: Brian Sambeldin explains how Java can be effectively used for data science, emphasizing the gap between Python experimentation and production-ready Java deployment. He highlights Jupyter notebooks for interactive experimentation, building reproducible data science workflows, and integrating with Java via JShell and Docker-based Java kernels. The talk also covers creating a Java data science stack with libraries like DJL, DF Lib, and others, enabling developers to perform analytics, machine learning, and deep learning entirely in Java while maintaining enterprise-grade production readiness.
Spring Boot 4 OpenTelemetry: From Zero to Full Observability in Minutes: The author explains how Spring Boot 4 introduces a new OpenTelemetry starter for seamless observability, letting developers automatically collect logs, metrics, and traces without pulling in the full actuator. Using Docker Compose with the Grafana LGTM stack, users can quickly visualize traces, metrics, and logs, including trace and span IDs for multi-step requests. Spring Boot 4 also allows adding custom metrics via annotations or the observation registry, and logs can now be exported through OpenTelemetry, giving developers end-to-end visibility into production behavior and making observability easier and more integrated.
Virtual Threads in the Real World: Fast, Robust Java Microservices with Helidon: The author explains how Helidon leverages Java virtual threads to simplify building highly concurrent, high-throughput servers. Unlike traditional asynchronous designs, Heladon 4 rewrites its web server to use virtual threads end-to-end, allowing each request to run on its own virtual thread, which can block without affecting performance. This approach not only improves scalability—supporting millions of concurrent tasks—but also makes the code much easier to write, read, and debug compared to complex reactive or asynchronous patterns.
📚 Helpful Resources (6)
25+ Real-World Use Case-Based Java/Spring Boot Interview Questions
Everything Bundle (Java + Spring Boot + SQL Interview + Certification)
Thanks for reading this far! Consider becoming a paid subscriber and support the work :)
Not convinced? Check out the details of the past work
Gift
This repository is a goldmine of all the Java and ecosystem libraries
This free ebook about Scalable Enterprise Java for the Cloud is new in town.
This repository lists free resources related to Java books.