Spring Data JPA: How to bulk insert data
Discussing 3 Options to bulk insert data in RDBMS
Introduction
As a Software engineer who works primarily as a backend engineer or full-stack engineer, we often come across use cases where inserting data as bulk into the database is paramount.
Some of the use cases will be like backfilling newly modified tables with old table data, populating secondary database tables with the primary database, or even taking back up of actual data, etc.
In this article, we will discuss how we can insert data in bulk into the database using Spring Data JPA.
Consider becoming a free or paid subscriber and support the work :)
Still not convinced? Check out the details of the past work
Entity
For this example, we are using the Accounts table as shown below. This table gets a unique primary key Id from the accounts_seq generator.
The repository interface extends from JpaRepository which provides many out-of-the-box methods to deal with the database easily.
Option 1
JpaRepository extends from ListCrudRepository which provides saveAll method.
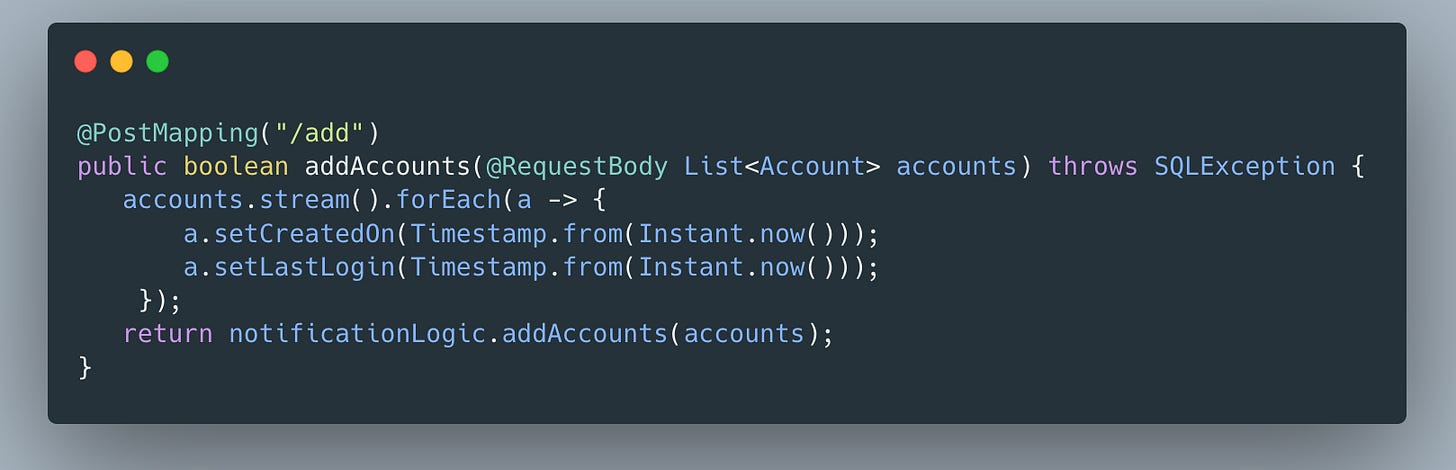
In this option, we will save a list of accounts using this method that will persist in the list of accounts in the accounts table.
Our controller receives a list of accounts as @RequestBody.
We can send an array of accounts as JSON in the request body.
Once we hit the endpoint, our insert logic gets executed, I have enabled JPA logs to see the query.
Our database is updated with recent insertion of records.
As we can see in the query logs saveAll executes one query for each record and does not insert everything in one query using INSERT INTO VALUES.