Engineering With Java: Digest #75
Java prediction for 2026, ForkJoinPool shenanigans, API versioning, abstracting data access, BDD with Java & MongoDB and more ...
👋 Java Devs! Welcome to this week’s addition! I hope you’re all doing great. This edition is special because i am excited to share two updates with you all.
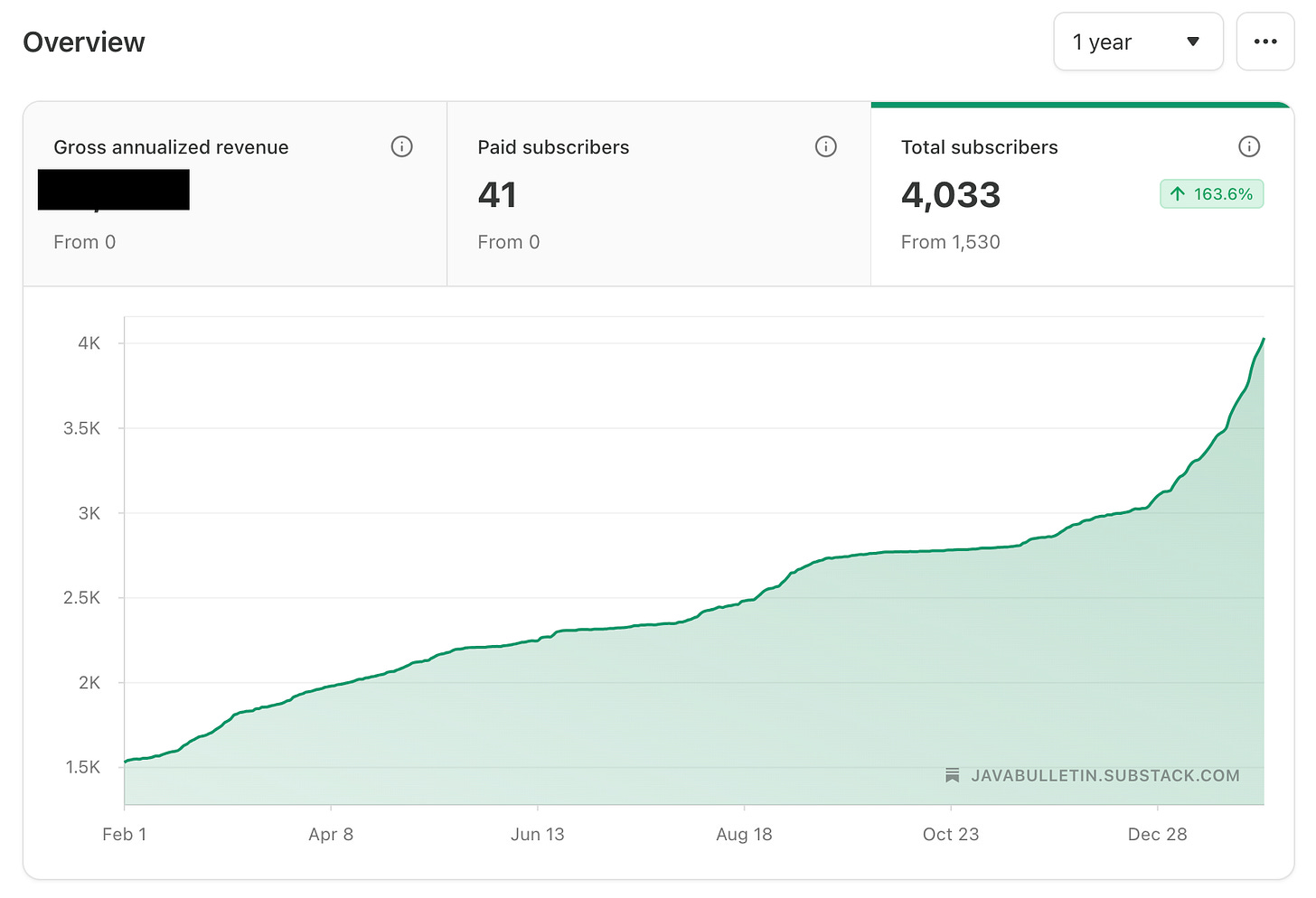
We crossed 4k subscribers 🎉 , and 41 subscribers considered the work paid worthy. Thanks for all the supports. You guys are awesome ❤️
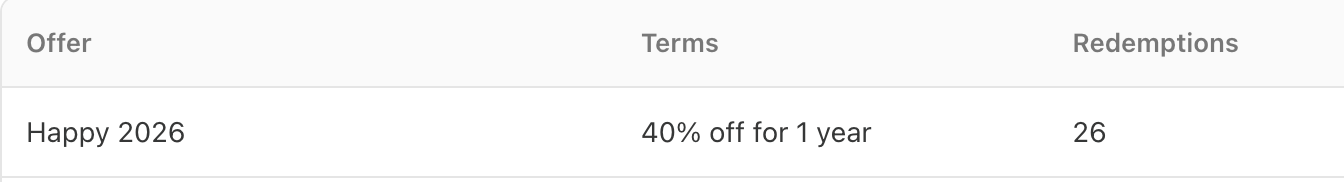
We had huge success with 40% discount on our annual subscription i.e $18/year offer. 26 readers took the advantage of it. We are wrapping the discounts in few hours. If you are interest, Grab it before it ends.
(If you have any question reach out to surajmishra150893@gmail.com or DM me in substack app)
This week, we cover essential insights on:
But before we kick off , meme of the week 😊
🗒️ Articles Of The Week (10)
A Java Champion Explains His Java Predictions for 2026 : Java Champion Simon Ritter shares key predictions for where Java is headed by 2026, including its role as the backbone of scalable enterprise AI, the rising compute demands that AI-powered workloads will place on JVM apps, and the likelihood that AI-assisted coding will grow while experienced developers remain essential. He also expects a shift from simple cloud migrations to deeper “Java modernization” efforts driven by cost, risk, and AI integration. These trends highlight Java’s continued strength in large-scale, mission-critical systems
ForkJoinPool shenanigans : This article explains a small but impactful improvement in Java 25’s concurrency support: the common ForkJoinPool now has a new internal method asyncCommonPool() that ensures there are always threads available even if the common pool’s parallelism was set to zero, avoiding dangerous fallbacks that used to spawn a new thread per task. It also notes that ForkJoinPool now implements ScheduledExecutorService, letting us use the common pool as a global timer, and that these changes make APIs like CompletableFuture safer and more predictable in concurrent Java code.
How to Conditionally Skip Tests in TestNG : This guide shows how to conditionally skip TestNG tests by using annotations and logic rather than just deleting or disabling them manually. It covers using enabled = false, runtime checks inside @BeforeMethod, and TestNG’s SkipException to programmatically skip tests based on conditions like environment flags, data values, or configuration. The result is cleaner, more flexible test suites that run only what’s relevant for a given build or environment.
Abstracting Data Access in Java With the DAO Pattern : This article breaks down how the DAO (Data Access Object) pattern helps cleanly separate persistence logic from business logic in Java applications. By defining repository‑style interfaces and concrete implementations for data operations, we make code easier to test, maintain, and swap out underlying storage without touching core logic. The piece also walks through practical examples showing how DAOs support clear abstraction and promote cleaner architecture.
Overview of MCP Annotations in Spring AI : This article explains how Spring AI uses MCP (Model Context Protocol) annotations to let us declaratively expose Java methods and data to AI models, removing a lot of boilerplate and manual registration. Core server‑side annotations like @McpTool, @McpResource, and @McpPrompt turn normal Spring methods into callable AI tools, resources, or prompt templates, while others like @McpComplete support auto‑completion and richer client experiences. On the client side, MCP annotations help handle notifications and events from MCP servers. Using these annotations makes building AI‑integrated Spring applications clearer and more maintainable
Implementing API Versioning in Spring : This tutorial walks through API versioning strategies in Spring, showing how we can evolve REST endpoints without breaking existing clients. It covers common approaches like using URI paths (e.g., /v1/…), request headers, and @RequestMapping media types to support multiple versions in the same application. The goal is clear: enable safe, structured API evolution so we can introduce new features while still supporting older versions.
How to Find Matched Rules in Drools : This article shows how to inspect which rules matched and fired in a Drools rules engine session, helping us understand why certain decisions were made. It walks through using listeners like AgendaEventListener and RuleRuntimeEventListener to capture matches and activations, then shows how to log or collect these rule hits so we can debug, audit, or explain rule behavior in a running system.
Introduction to Behavior Driving Development with Java and MongoDB : This article introduces Behavior‑Driven Development (BDD) with Java and MongoDB by showing how we can use readable scenarios to guide development and tests. It walks through defining behaviors in domain terms, implementing steps with Java code, and wiring them up to MongoDB data operations so test expectations drive the design. The result is clearer requirements, better test coverage, and software that more closely matches desired behavior.
Bootstrapping a Java File System : This article walks through how to bootstrap and interact with a file system in Java using the java.nio.file API, showing how to create, traverse, and manipulate directories and files in a clean, modern way. It highlights key classes like Path, Files, and FileSystem, explains how file systems can be abstracted or even customized, and gives practical examples to make file operations safer and more expressive than older java.io approaches.
Implement Multitenancy in Spring Authorization Server : This article explains how to implement multitenancy in Spring applications, letting one codebase safely serve multiple tenants with isolated data. It walks through different strategies — like separate databases, separate schemas, or shared schemas with discriminator columns — and shows how Spring can resolve the correct tenant at runtime using filters or interceptors. The goal is to structure the app so tenant‑specific context flows through repositories and services without scattering tenant logic everywhere.
🔥 Recently Published In-house Blogs (6)
Spring Boot Interview Question – Securing Sensitive Fields in Records
Java Interview Question - Why you should not use static initializers?
Spring Boot Interview Question - Process Large Security Events File
Spring Boot Interview Question - Fix Magic Number Code Smell /Dynamic Reload
Java Interview Question - Can You Modify a Final Field using Reflection?
▶️ Videos Of The Week (2)
Scripting Java, Collections & Generics, BeJUG : Authors reflect on how Java’s long-term design choices—around collections, generics, and type erasure—favored pragmatic compromises over theoretical purity, keeping the language and APIs usable and evolvable at scale. We also see how modern Java has quietly become more lightweight and script-friendly, making it suitable for everyday automation as well as large systems. Tying it all together is the role of the community, where sustainable Java ecosystems emerge not from perfection, but from shared ownership, practical decisions, and steady evolution over time.
Production-Grade Null Safety in Spring Boot 4 : This walkthrough shows how many production null pointer exceptions come from missing contracts rather than bad logic, and how we can push those failures from runtime to build time. By combining JSpecify annotations to clearly declare nullability and NullAway to strictly enforce those rules via the compiler, we make null handling explicit, visible, and unavoidable. The result is safer Spring Boot applications where null-related bugs are caught early, long before they surprise us in production.
🧑💻 Jobs Of The Week (5)
📚 Useful Links (5)
39+ Real-World Use Case-Based Java/Spring Boot Interview Questions
Everything Bundle (Java + Spring Boot + SQL Interview + Certification)
Thats all for this week! Thanks for reading this far. If you liked it please share with your network.



Excellent roundup! The ForkJoinPool asyncCommonPool improvement actually solves a nasty edge case I ran into last year where setting parallelism to zero caused unpredictable thread spawning under load. Having it implemnt ScheduledExecutorService is clever too since most apps already have timing logic scattered across custom schedulers. Consolidating that into the common pool could simplfy a lot of production code.